 Getty Photographs
Getty PhotographsWith insurgent forces now contained in the Syrian capital Damascus, and reviews that President Bashar al-Assad has fled the nation, anti-government forces seem to have introduced concerning the finish of his regime lower than a fortnight after their lightning offensive started.
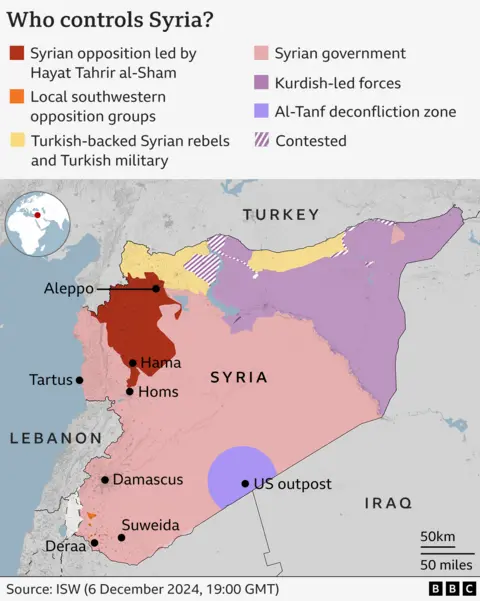
Islamist fighters took management of the northern metropolis of Aleppo in late November earlier than swinging south by means of Hama and Homs – areas beforehand below authorities management.
In southern Syria, near the Jordanian border, native rebels have captured many of the Deraa area, the birthplace of the 2011 rebellion in opposition to Assad.
In lots of situations, it’s reported that the Syrian army both left their posts or defected to the opposition.
The preliminary assault was led by the Islamist militant group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) – which has an extended and concerned historical past within the Syrian battle.
HTS is designated as a terrorist organisation by the UN, US, Turkey and different international locations.
Who’re Hayat Tahrir al-Sham?
 Reuters
ReutersHTS was arrange below a distinct title, Jabhat al-Nusra, in 2011 as a direct affiliate of Al Qaeda.
The chief of the self-styled Islamic State (IS) group, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, was additionally concerned in its formation.
It was considered probably the most efficient and lethal of the teams ranged in opposition to President Assad.
However its jihadist ideology gave the impression to be its driving power quite than revolutionary zeal – and it was seen on the time as at odds with the principle insurgent coalition below the banner of Free Syria.
And in 2016, the group’s chief, Abu Mohammed al-Jawlani, publicly broke ranks with Al Qaeda, dissolved Jabhat al-Nusra and set up a new organisation, which took the title Hayat Tahrir al-Sham when it merged with a number of different comparable teams a yr later.
For a while now, HTS has established its energy base within the north-western province of Idlib the place it’s the de facto native administration, though its efforts in the direction of legitimacy have been tarnished by alleged human rights abuses.
It has additionally been concerned in some bitter infighting with different teams.
Its ambitions past Idlib had change into unclear.
Since breaking with Al Qaeda, its purpose has been restricted to making an attempt to determine fundamentalist Islamic rule in Syria quite than a wider caliphate, as IS tried and did not do.
It had proven little signal of making an attempt to reignite the Syrian battle on a serious scale and renew its problem to Assad’s rule over a lot of the nation – till now.
Why is there a battle in Syria?
In March 2011, pro-democracy demonstrations erupted within the southern metropolis of Deraa, impressed by uprisings in neighbouring international locations in opposition to repressive rulers.
When the Syrian authorities used lethal power to crush the dissent, protests demanding the president’s resignation erupted nationwide.
The unrest unfold and the crackdown intensified. Opposition supporters took up arms, first to defend themselves and later to rid their areas of safety forces. Mr Assad vowed to crush what he referred to as “foreign-backed terrorism”.
Lots of of insurgent teams sprang up, overseas powers started to take sides and extremist jihadist organisations such because the Islamic State (IS) group and al-Qaeda, turned concerned.
The violence quickly escalated and the nation descended right into a full-scale civil battle drawing in regional and world powers.
Greater than half one million folks have been killed and 12 million have been pressured to flee their properties, about 5 million of whom are refugees or asylum seekers overseas.
How did the insurgent offensive come about?
The battle in Syria had for the previous 4 years felt as if it have been successfully over.
President Bashar al-Assad’s rule had primarily been uncontested within the nation’s main cities, whereas another components of Syria remained out of his direct management.
These embrace Kurdish majority areas within the east, which have been kind of separate from Syrian state management because the early years of the battle.
There had been some continued, although comparatively muted unrest, within the south the place the revolution in opposition to Assad’s rule started in 2011.
Within the huge Syrian desert, holdouts from the group calling themselves Islamic State nonetheless pose a safety menace, notably throughout the truffle searching season when folks head to the world to seek out the extremely worthwhile delicacy.
And within the north-west, the province of Idlib has been held by militant teams pushed there on the top of the battle.
HTS, the dominant power in Idlib, is the one which has launched the shock assault on Aleppo.
For a number of years, Idlib remained a battleground as Syrian authorities forces tried to regain management.
However a ceasefire deal in 2020 brokered by Russia, which has lengthy been Assad’s key ally, and Turkey, which has backed the rebels, has largely held.
About 4 million folks reside there – most of them displaced from cities and cities that Assad’s forces gained again from rebels in a brutal battle of attrition.
Aleppo was one of many bloodiest battlegrounds and represented one of many rebels’ largest defeats.
To realize victory, President Assad couldn’t depend upon the nation’s under-equipped and poorly motivated conscript military alone, which quickly turned dangerously stretched and commonly unable to carry positions in opposition to insurgent assaults.
As an alternative, he got here to rely closely on Russian airpower and Iranian army assistance on the bottom – primarily by means of militias sponsored by Tehran.
These included Hezbollah.
There may be little doubt that the setback Hezbollah has suffered lately from Israel’s offensive in Lebanon, in addition to Israeli strikes on Iranian army commanders in Syria, has performed a big half within the resolution by jihadist and insurgent teams in Idlib to make their sudden, surprising transfer on Aleppo.
Prior to now few months, Israel has intensified its assaults on Iranian-linked teams in addition to their provide strains, inflicting severe harm on the networks which have saved these militias, together with Hezbollah, operative in Syria.
With out them, President Assad’s forces have been left uncovered.
Extra reporting by Maia Davies.



















































