Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia – In one in every of his first appearances of the 12 months, South Korean President Yoon Seok Yeol pledged to spice up confidence within the nation’s inventory market, which is famed for being undervalued in contrast with its friends.
Because the curtain closes on 2024, Yoon has achieved the alternative, rattling markets with a short-lived declaration of martial regulation that has thrown Asia’s fourth-largest economic system into its greatest political disaster in many years.
“South Korea is meant to be the bulwark,” Geoffrey Cain, the writer of Samsung Rising and a managing accomplice at Alembic Companions, instructed Al Jazeera, describing the nation as an exception to rising authoritarianism in a area the place China’s affect looms massive over economies from Hong Kong to Taiwan.
“However even its economic system is just not protected from political interference. Martial regulation spooked the markets and this exhibits that South Korea is just not as steady as market analysts typically assume.”
With the Nationwide Meeting poised to vote on Yoon’s impeachment on Saturday, the president’s future hangs within the stability.
Yoon has rebuffed calls to step down, and the chief of his conservative Folks Energy Occasion (PPP) on Thursday introduced that he would oppose the impeachment effort, casting doubt on its possibilities of success.
PPP chief Han Dong-hoon instructed reporters that whereas he couldn’t defend Yoon’s “unconstitutional” declaration of martial regulation, he would search to unify his get together in opposition to the movement to forestall “chaos”.
With the centre-left Democratic Occasion (DP) and different opposition factions holding 192 seats within the 300-member Nationwide Meeting, the opposition bloc wants a minimum of eight conservative legislators to cross the aisle so as to attain the two-thirds threshold required for impeachment.
If the movement is profitable, South Korea’s Constitutional Court docket would then rule on whether or not to verify Yoon’s elimination from workplace – a course of that will doubtless take months.

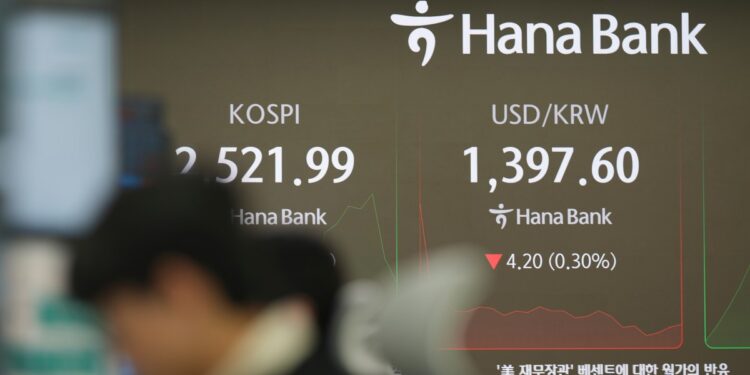
South Korea’s benchmark inventory index, the KOSPI, fell as a lot as 0.9 % in early buying and selling on Thursday, after closing 1.44 % decrease yesterday.
South Korea’s gained fell to a two-year low in opposition to the US greenback on Wednesday earlier than recovering a lot of the bottom it misplaced.
“The market response to this point has been modest. It seems that the Korean authorities is mobilising a contingency plan and it stays to be seen how briskly it might deliver issues again to regular,” Yeo Han-koo, a former South Korean commerce minister who’s now a senior fellow on the Peterson Institute for Worldwide Economics, instructed Al Jazeera.
“If the political turmoil is extended, that would negatively have an effect on the arrogance of traders, customers and patrons, although. The stabilisation of the political atmosphere can be critically vital.”
Whereas the fallout has been comparatively contained to this point, a protracted standoff can be the worst consequence for South Korea’s monetary markets and the broader economic system, analysts say.
“I feel the hazard may happen if the president decides to dig in, refuses to resign and his get together doesn’t vote for impeachment,” Gareth Leather-based, senior economist for Asia at Capital Economics, instructed Al Jazeera.
Leather-based stated Thailand, which has been racked by political turmoil since a 2006 coup, is an instance of how dysfunctional management can stifle the economic system.
“The dispute between the 2 sides hasn’t actually gone away although it’s 18 years on,” Leather-based stated.
“And you may see fairly clearly from the info there that it has actually affected the economic system, that funding has been tremendous depressed, that progress has actually struggled and a big a part of that may be traced again to the political dysfunction that bedevils the nation.”
Whereas South Korea is dwelling to globally famend company giants akin to Samsung and Hyundai, shares of South Korean corporations have lengthy been seen as undervalued in contrast with their international friends.
Apple’s market capitalisation is a few 14 occasions the scale of that of Samsung Electronics, the crown jewel of the sprawling Samsung Group, regardless of its revenues being solely a couple of third greater than its Korean rival.
The so-called “Korea low cost” has been attributed to a number of components, together with the nation’s proximity to North Korea and poor company governance on the family-run “chaebol” that dominate the economic system.
After Yoon’s pledge in January to undertake “daring” reforms to spice up the inventory market, his administration rolled out a sequence of measures, together with an index specializing in corporations which have improved capital effectivity and tax advantages for corporations that enhance shareholder returns.
Regardless of some preliminary optimistic response from traders, the measures did little to raise the market.
Even earlier than Yoon’s martial regulation declaration unnerved traders, the KOSPI was down about 14 % in contrast with July.
The inventory market’s weak efficiency comes as South Korea’s economic system is faltering, amid slowing demand in China and expectations of hefty tariffs beneath United States President-elect Donald Trump.
Gross home product grew simply 0.1 % through the July-September interval, central financial institution knowledge confirmed on Thursday, following a 0.2 % contraction through the earlier quarter.
Final 12 months’s progress price of 1.4 % was the weakest efficiency, excluding the COVID pandemic, for the reason that aftermath of the 2008 international monetary disaster.

“This incident gained’t do lasting harm, however it’s going to spook folks,” Cain, the writer, stated, including that South Korea’s standing as an financial powerhouse “isn’t assured perpetually”.
“South Korea now has to cope with longer-term issues of a collapsing workforce inhabitants, export competitors from Taiwan, geopolitical threats from China, and a deindustrialising economic system.”
Nonetheless, regardless of the political uncertainty and financial headwinds, analysts level to South Korea’s sturdy financial fundamentals and establishments as a trigger for optimism.
“The swift rejection of martial regulation by the Nationwide Meeting and the general public makes me hopeful – there stay for now sturdy institutional checks, excessive civic engagement, and democratic safeguards,” Pushan Dutt, a professor of economics and political science on the Singapore campus of enterprise college INSEAD, instructed Al Jazeera.
“Proper-wing populists have held Viktor Orban as a mannequin. In an period of democratic backsliding, South Korea can be held up as a mannequin.”
Soohyung Lee, a member of the Financial Coverage Board on the Financial institution of Korea and a professor at Seoul Nationwide College, stated she doesn’t consider the present political disaster may have an enduring destructive impact on the nation’s economic system or fame.
“Whereas the occasion was surprising and launched some uncertainty, it additionally highlighted the energy of South Korea’s rule of regulation,” Lee instructed Al Jazeera, stressing that her views don’t essentially mirror the official positions of the Financial institution of Korea or Seoul Nationwide College.
“The swift and orderly response demonstrated that the nation is supplied to deal with unexpected political challenges with out permitting any particular person or small group to derail the system.”
South Korea has emerged from adversity in a stronger place earlier than, Lee stated, pointing to the nation’s swift recoveries from the 1997 Asian monetary disaster and the 2008 international monetary disaster.
“Drawing on this historical past of resilience and adaptableness, I stay optimistic about the way forward for the Korean economic system,” Lee stated.
Yeo, the previous commerce minister, stated many developed international locations have lately skilled challenges to their democracy.
“I feel that any nation may very well be uncovered to this sort of dangers. I feel there exist each ‘Korea premium’ in addition to ‘Korea low cost’,” he stated.
“Korea has energy in its cultural tender energy, excessive tech and manufacturing sectors, but additionally weak point in political and geopolitical pressure and company governance, and many others. It’s all about the best way to capitalise on such ‘Korea premium’, whereas rectifying ‘Korea low cost’.”